Description
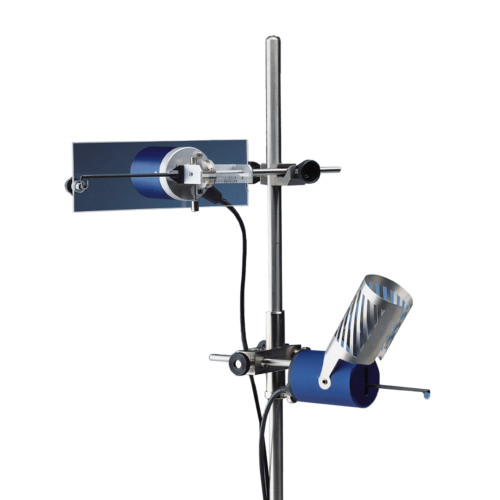
Le Générateur ECT (Electro Convulsive Therapy) est spécialement conçu pour la recherche neurochimique et neuropharmacologique.
Une sortie à courant constant est utilisée, ce qui garantit des résultats reproductibles et une détermination précise du seuil EC tout en identifiant également toutes les variations du seuil provoquées par des médicaments ayant une action spécifique sur le cortex et les régions sous-corticales. Les paramètres de choc ont été sélectionnés après consultation de la littérature la plus pertinente, afin de fournir la plage la plus adaptée lors d’opérations avec des souris ou des rats.
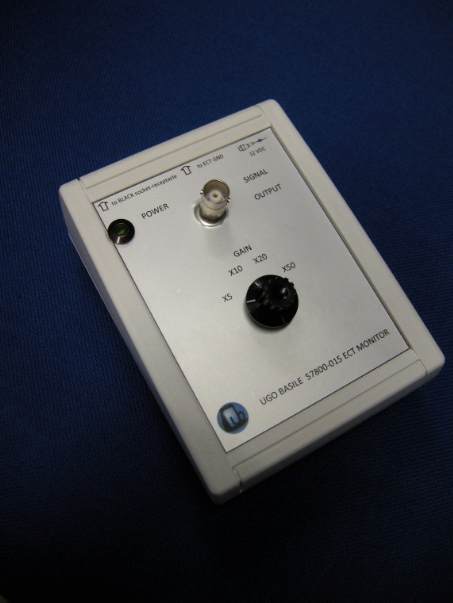
Des niveaux de courant reproductibles cohérents sont produits par des circuits de rétroaction qui ajustent la variance de l’impédance du contact d’un animal à l’autre.
L’impédance de l’animal peut être pré-mesurée et affichée, et un signal d’avertissement clignote si l’impédance est trop grande pour fournir le niveau de courant souhaité.
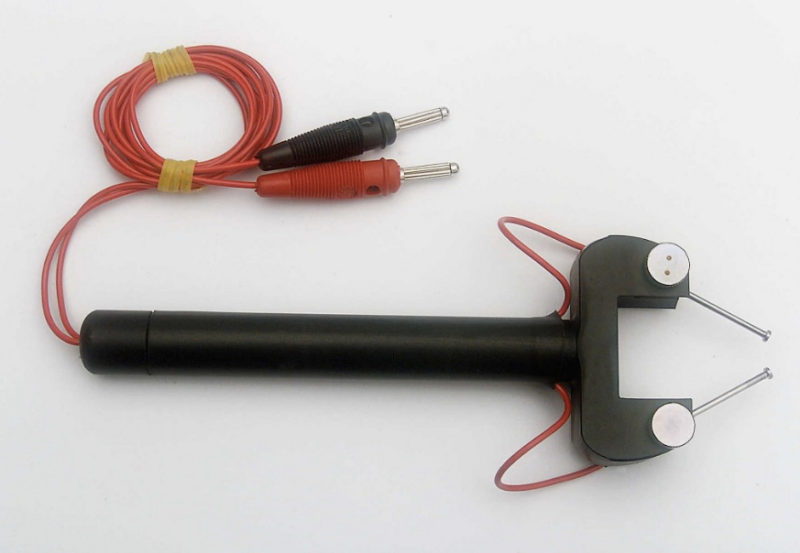
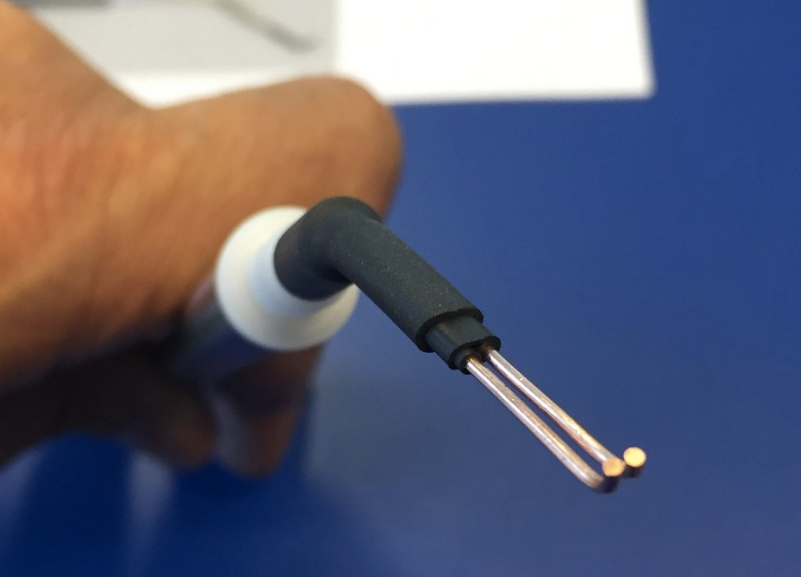
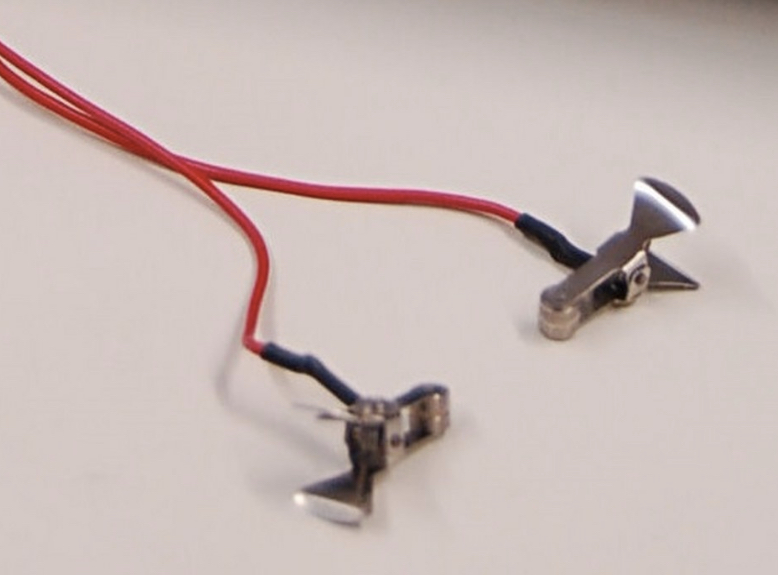
Les électrodes auriculaires standard fournies (voir photo principale) permettent à un seul opérateur de délivrer un choc à un certain nombre de sujets en peu de temps. Des électrodes cornéennes en option sont disponibles en option.
Le circuit de sortie spécial permet d’utiliser tout type d’électrode.